Africa: The New Hub for Automotive Manufacturing
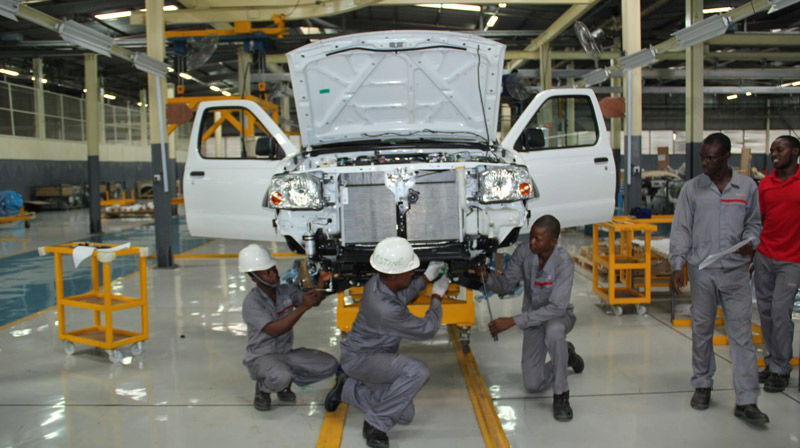
The automotive manufacturing industry in Africa is growing fast. Automotive production in Africa is growing industry as more and more manufacturers move closer to their African customers and discover the advantages of low-labour costs and tax holidays. Demand for automobile spare parts in Africa is also growing. The automotive production industry in South Africa is nearly 100 years old. In the 1980s and 1990s, Nigeria achieved significant production and production occurs in Egypt and more recently Morocco. Smaller production activities take place in Kenya and some decades ago in Zimbabwe. However, currently significant modern assembly is largely located in South Africa.
Formed in 2015, the Africa Association of Automotive Manufacturers (AAAM) works specifically to promote and facilitate the growth of the African automotive industry. Formed by executives from the world’s biggest car manufacturers, the African Association of Automotive Manufacturers (AAAM) embarked on a concerted push to revive and resurrect Africa’s auto industry. Since then, the newly-created African Association of Automotive Manufacturers (AAAM) has been working with key African governments to create the right policy environment for the sector to Flourish.
 Africa’s untapped demand combines with a steady increase in consumer spending which has been rising at an annual rate of 10 per cent over the last few years. Moreover, analysts predict that by 2030, over half a billion Africans will have joined the middle class. “If the growth in vehicle sales keeps pace with growing consumer spending, annual sales of passenger cars in Sub-Saharan Africa will surpass 10 million units by 2030,” says South African consultancy B&M Analysts.
Africa’s untapped demand combines with a steady increase in consumer spending which has been rising at an annual rate of 10 per cent over the last few years. Moreover, analysts predict that by 2030, over half a billion Africans will have joined the middle class. “If the growth in vehicle sales keeps pace with growing consumer spending, annual sales of passenger cars in Sub-Saharan Africa will surpass 10 million units by 2030,” says South African consultancy B&M Analysts.
Not surprisingly, one of the organisation’s first ports of call was government leaders in Nigeria’s capital Abuja. Fast-growing Nigeria is the jewel in Africa’s auto crown with just 44 vehicles per 1,000 inhabitants,far below the global average of 180 vehicles per 1,000 inhabitants, according to recent estimates by a Deloitte report.
While new vehicle sales have jumped in developing markets like China, India and Brazil over the last decade, growth in Africa has remained relatively slow. According to the International Organisation of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers (OICA), only 1.5 million new vehicles were sold across the African continent’s 54 countries with a combined population of 1.3 billion. South African consumers buy most new cars, and together with Egypt, Algeria and Morocco account for almost 80 per cent of the continent’s total auto sales, with only muted demand from important economies like Nigeria and Kenya.
But far from being a disincentive to investors, the figures act as a rallying call. “When Volkswagen and General Motors moved into China the motorisation rate was lower than in Ethiopia today. The limited market was not a deterrent for the early movers who recognised China’s long-term potential,” says Karthi Pillay, Africa automotive leader, risk advisory at Deloitte.
Mix with this a renewed determination amongst African leaders to diversify their economies through boosting manufacturing. New policies aimed at increasing domestic car production are starting to pay off. In 2016, China’s state-owned car manufacturer Beijing Automotive International Corp unveiled plans to build a R11bn (US$759mn) auto plant in South Africa – the biggest investment in a vehicle-production facility in the country in four decades will earmark over half of its output for export, initially to East, West and North Africa. Elsewhere, after a four-decade break in production, Volkswagen is starting up its Kenyan production line once again.
The signs are good. But with challenges ranging from imported used cars flooding the market to Africa’s weak manufacturing base and a lack of finance for would-be car owners, Africa promises a challenging operating environment.
IMPORT OF USED CARS IN AFRICA
The biggest barrier to new vehicle sales in Africa is cheap, imported second-hand cars from the US, Europe and Japan. Consultancy Deloitte estimates that eight out of 10 imported cars in Ethiopia, Kenya and Nigeria are used cars. According to the Kenya National Bureau of Statistics (KNBS) in 2021 Kenya imported $549 million in Cars, mainly from Japan ($423 million), United Kingdom ($51.4 million), South Africa ($14.9 million), Thailand ($9.8 million), and India ($8.88 million).
Governments are developing policies to limit the influx. In an effort to hike the price of second-hand cars to favour more new car purchases, Kenya has forbidden vehicles over eight years old from entering into the country, with plans to reduce this further. Similarly, Nigeria has increased its import duty on second-hand vehicles, most of which arrive in a bustling trade from the US into Africa via Benin’s Cotonou port. As a result, Nigeria’s imports of cars from the US plummeted from more than 100,000 a year to less than 30,000 units in 2023.
 Nigeria car salesOther signs of change include the enduring stagnation of the Japanese economy. It has resulted in sluggish sales of new cars there, which in turn has created a shortage in the supply of quality used vehicles. There has been “a deterioration of the environment surrounding the export of the used motor vehicles industry”, says Hiroshi Sato, chairman of the Japan Used Motor Vehicle Exporters Association.
Nigeria car salesOther signs of change include the enduring stagnation of the Japanese economy. It has resulted in sluggish sales of new cars there, which in turn has created a shortage in the supply of quality used vehicles. There has been “a deterioration of the environment surrounding the export of the used motor vehicles industry”, says Hiroshi Sato, chairman of the Japan Used Motor Vehicle Exporters Association.
As crucial as controlling used-car imports is to nurturing a domestic industry, so is establishing a manufacturing base. South Africa leads the continent’s auto manufacturing sector with original equipment manufacturers, long-established in the country and backed by a vibrant community of 500 suppliers and diversi?ed manufacturers. Yet, head up the continent and there is little auto manufacturing until North Africa, bar light manufacturing from imported kits.
Kenya only has three assembly plants, and they all produce vehicles with wholly imported parts that require no domestic manufacturing input.
The Kenyan government, which has identified the auto sector as a key driver of the country’s industrialisation policy, has promised incentives to encourage a local industry. These include building special economic zones which benefit from tax holidays and low utility rates.
It has also introduced local input requirements and tariffs on imported auto components that could be manufactured locally. Encouragingly, the assembly of motor vehicles in Kenya grew by 31.4% from 2021 to 2023, with assembly figures forecast to almost double between 2013 and 2019. It’s improving the country’s chances of becoming a hub for assembly and production in the region.
It’s a similar story in Nigeria, where the Automotive Industry Development Plan (NAIDP) pledges to build auto industry infrastructure including supplier parks and clusters. Tax incentives include Nigeria allowing car groups to import two fully-built units at a discount duty of 35 per cent for cars and 20 per cent for commercial vehicles, for every one built locally. The government also aims to boost skills and investment and encourage a local component industry to supply manufacturers at competitive prices. It amounts to the kinds of incentives that encouraged Ford to begin assembling its Ford Ranger pickup in the Nigerian city of Ikeja in 2015, partnering with Ford dealer group Coscharis Motors on the project.
“Nigeria is a priority market for us in Sub-Saharan Africa and this will allow us to better serve our customers, both from a retail point of view and in terms of vehicle and parts availability,” says Jeff Nemeth, president and CEO of Ford Motor Company of Sub-Saharan Africa. “We are committed to supporting Nigeria’s developing automotive industry and economy together with Coscharis, and are looking forward to being active in the community. New assembly operations, even on a smaller scale like this one, have very positive ripple effects in the local economy and workforce.”
But nurturing indigenous manufacturing is still difficult. Nigeria-based groups Nissan and Peugeot also only assemble the bulk of their vehicles from imported semi-knocked down (SKD) kits because there is no local manufacturing industry. Even Nigeria’s own Innoson Vehicle Manufacturing Company (IVM) based in the south-eastern Anambra state, assembles trucks and buses with completely knocked-down (CKD) kits with all the vehicles’ engines, gear boxes and electrical parts imported from overseas. Auto-related imports into Nigeria accounted for around 10% of total imports, worth around US$6.5 billion in 2023, according to UNCTAD.
THE AUTOMOTIVE SECTOR IN AFRICA
Nigerian policy is currently making things even more difficult. Like all manufacturing, the auto sector is struggling under currency policies and associated import controls set up to conserve hard currency – and encourage local manufacturing – by prioritising strategic imports. It’s starving the auto sector of inputs and leading to a collapse in supplies of product lines from glass to rubber. OICA estimates that total new vehicle sales in Nigeria dropped by more than half in 2023, compared to 2020. It’s this kind of foreign exchange controls that are also limiting the ability of companies to import SKD units and parts for assembly and repair in Ethiopia, where high taxes also make cars unaffordable for most.
Exporting within Africa is also a challenge for the continent’s carmakers because of tariffs and barriers. Uganda and Tanzania slap tariffs on cars assembled in Kenya, the only country in the East African Community with assembly capability, because they don’t meet local input criteria. It gives imported second-hand cars the edge.
In recent times, Toyota South Africa saw a fall in exports to the rest of the continent as a result of higher tariffs in Nigeria, Algeria and Angola. Meanwhile, South Africa exports more vehicles to Europe, the US and even Asia than it does to its neighbouring African market. “Vehicle exports to Europe and Asia continued to show growth. Vehicle exports to African markets recorded substantial declines. This was due to a combination of factors including ad hoc duty increases in Nigeria and Zimbabwe, regulatory restrictions in Algeria and weaker economic conditions across most African countries due to the decline in commodity prices,” says Nico Vermeulen, director of the National Association of Automobile Manufacturers of South Africa (NAAMSA).
AFRICA: CAR FINANCE PROBLEMS
Governments also need to create easier access to car finance. “The availability of financing for new motor vehicles is virtually non-existent in most African countries,” says Vermeulen.
South African banks have been quickest off the mark. South Africa’s FirstRand Bank announced plans to set up a vehicle financing arm in Nigeria via its subsidiary WesBank, Sub-Saharan Africa’s largest provider of auto loans.
 Meanwhile, First Bank of Nigeria has spotted opportunity in the growth of car sharing in Nigeria in a development that the architects trying to build demand for new cars can hardly welcome. The bank’s vehicle ?nancing arm plans to extend borrowing to highly-rated Uber drivers via low-interest, used vehicle loans. The car-sharing platform has operated in Abuja and Lagos since it entered the Nigerian market in 2014. It currently has more than 2,000 drivers and was targeting 10,000 by the end of 2025.
Meanwhile, First Bank of Nigeria has spotted opportunity in the growth of car sharing in Nigeria in a development that the architects trying to build demand for new cars can hardly welcome. The bank’s vehicle ?nancing arm plans to extend borrowing to highly-rated Uber drivers via low-interest, used vehicle loans. The car-sharing platform has operated in Abuja and Lagos since it entered the Nigerian market in 2014. It currently has more than 2,000 drivers and was targeting 10,000 by the end of 2025.
“We are absolutely committed to making it as easy as possible for our driver partners to start and maintain their own successful and pro?table businesses,” says Ebi Atawodi, general manager of Uber Nigeria. “And these used vehicle ?nance options make it possible for those with a demonstrable performance commitment to build sustainable businesses without incurring the high costs often associated with new vehicle purchases.”
The growth in car sharing in Nigeria leads Deloitte’s Pillay to ponder future developments in the industry. “It shows mobility leapfrogging car ownership; Africa may not be a market focused on making and selling cars,” he suggests.
Indian and Chinese manufacturers believe their low-cost models will have the advantage, while others are betting on the electric car. Uganda’s Kiira Motors grew out of a research project at Makerere University and is aiming to produce electric vehicles by 2019 before becoming original manufacturers by 2039. Ford is expanding its multi-modal approach to urban mobility. One of the innovations on show at Go Further Africa was its electric MoDe:Pro e-bike.
Whatever the future holds, Africa’s consumers are the last untapped market for the auto giants.